China's new 2010 GMP requires that all pharmaceutical companies require clean validation of their production equipment. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) analysis is a very suitable analytical method for cleaning validation. Compared with the traditional HPLC method, TOC method is more sensitive and can be detected even for a few water-insoluble organic compounds. And verification process is simple and convenient, no need to set other parameters.
Verification Overview
Chinese medicine extraction workshop, Chinese medicine preparation workshop, as well as collinear production of a variety of varieties of production equipment, in order to ensure that the pharmaceutical production process to minimize pollution and cross-contamination risk, according to GMP (2010 edition) requirements, must develop collinear production Equipment cleaning verification program. This shows the importance of cleaning validation.
For easy wiping and surface smoothing equipment, cotton swab method; easy to wipe sampling equipment and piping, using the leaching method. According to the specific circumstances of the equipment, to determine the operational cleaning method, according to different cleaning methods, by determining the limits of microbial and total organic carbon to determine the limits of residual pollutants.

Equipment cleaning Cleaning using a wipe method validation, the corresponding residues of the inspection, the use of swab wipe method to collect samples to check, add total organic carbon check dissolved in water to determine the total organic carbon diluted; , The corresponding residue inspection, collecting eluent as a test sample determination of total organic carbon.
By verifying the system applicability, linearity, accuracy and repeatability of the analytical method, it is confirmed that the method is suitable for the testing requirements of equipment cleaning verification and the sampling recovery rate verifies the effectiveness of the sampling method.
Verify the purpose
Through the TOC method validation, to ensure that the method can accurately and reliably detect the residual contaminants after collinear production equipment cleaning, to meet the expected limits. This is every pharmaceutical colleagues need to pay attention.
Validation range
It is suitable for the verification of the TOC measurement method of collected samples after the cleaning of collinear production equipment such as Chinese medicine extraction workshop and Chinese medicine preparation workshop.
Therefore, the TOC method of cleaning validation, in the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries, exactly how to define it?
◆ simplify the verification method based on the cleaning process rather than the product;
◆ rapid assessment of the cleaning process of cleaning capacity;
◆ Optimize key cleaning parameters (TACT, ie temperature, motion, concentration and time) by wiping and leaching sampling methods;
◆ Estimate the worst case scenario and complex ingredients such as detergents;
◆ speed up product replacement, better production according to plan.
TOC Act's unique advantages
For the TOC Act, organic matter can be well-tailored to determine whether any residual material is present, whether it is derived from products, cleaners, chemicals, solvents, by-products or microbial contamination This task. As long as the molecular structure contains carbon, any active pharmaceutical ingredient or cleaning residual material can be detected. The test results must be lower than the limit of the target compound, to improve the stringency of cleaning validation.
The TOC method has gradually been accepted by the pharmaceutical industry, and the stringency of clean validation in the entire industry has been significantly improved, more and more in line with the overall requirements of the industry. The pervasiveness of the TOC Act saves time and labor costs for pharmaceutical companies. Scientific, reasonable and feasible cleaning verification process to ensure the cleanliness required for the safe production of pharmaceuticals.
TOC law study notes
The first chapter TOC basic knowledge
First, what is TOC?
Second, why use TOC in cleaning verification and routine cleaning monitoring?
Third, the TOC in the verification of cleaning applications
Fourth, when can use TOC determination
Five, TOC method and commonly used methods of analysis
Chapter II Comparison of HPLC and TOC methods
Here for the HPLC and TOC to explain:
First, TOC and HPLC comparison
Second, the limitations of HPLC method
Third, TOC instead of HPLC
Fourth, the TOC advantage
Fifth, TOC to detect regulatory support
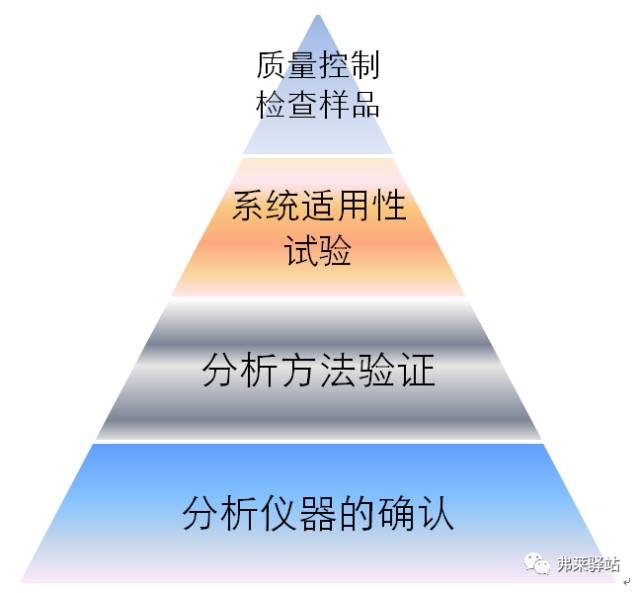
The third chapter TOC analysis method verification
First, the analysis method validation requirements
Second, TOC analysis method to verify the premise: TOC analyzer performance confirmation
Third, the system suitability test
Fourth, analysis of the key points of verification
Five, TOC method to verify the specific content
➤ Specific
➤ Linearity and Range
➤ Precision and accuracy
➤ Recovery test
Ø sampling method
Ø wipe recovery rate
Ø Wipe technology
Ø leaching recovery rate
Recycling rate of acceptance
➤ Minimum detectable limit (LOD), lowest limit of quantitation (LOQ)
Six, TOC analysis method of attention
The first chapter TOC basic knowledge
First, what is TOC ?
TOC method to detect the principle:
Total organic carbon (TOC), by a special instrument - total organic carbon analyzer (hereinafter referred to as TOC analyzer) to determine. TOC analyzer, the total organic carbon in aqueous solution is oxidized to carbon dioxide, and its content is measured. The use of carbon dioxide and total organic carbon between the corresponding relationship between carbon content in aqueous solution of total organic carbon for quantitative determination.
The TOC method includes the oxidation of carbon and the detection of generated carbon dioxide. There are a variety of oxidation technologies, including photocatalytic oxidation, chemical oxidation and high temperature burning.
Second, why use TOC in cleaning verification and routine cleaning monitoring?
Many pharmaceutical manufacturing sites currently use TOC for CV and monitoring
➤ Non-exclusive methods that theoretically detect all residual molecules that contain organic carbon and are easy to verify.
➤ Universal sample analysis methods: cleaning validation and validation, raw materials, and factory water
➤ Analyzes a wide range of dissolved, "insoluble" and most compounds commonly found in the pharmaceutical industry
➤ The TOC detects organic acrobatics and residues that are not completely clean in the device.
➤ Very good cost savings. Simple verification method, easy to train new users.
➤ Increase equipment turnaround time.
Third, the TOC in the verification of cleaning applications
➤ Determining the amount of detergent
➤ Determining the ingredients of a drug in combination with a specific assay
➤ TOC is used as a general indicator of cleanliness in order to establish a cleaning program
➤ Determination of the active ingredient
Fourth, when can use TOC determination
➤ Depending on the type of residue (detergent, active ingredient, excipient)
➤ Is the analyte water-soluble?
➤ Does the test object contain carbon?
TOC non-exclusive method, TOC determination is non-deterministic
➤ The TOC method determines all of the EO content in the sample
➤ The TOC method is only applicable to aqueous samples
➤ Units of measurement are expressed in ppb (ug carbon / L) and ppm (mg carbon / L)

Q: There is a question here. If it is an ester-soluble product, can the TOC method be used for cleaning verification testing?
A: By locating the literature and consulting related materials, TOC can detect organics that have low solubility in water, and the accuracy is good.
Five, TOC method and commonly used methods of analysis
➤ The TOC method, unlike HPLC and UV / Vis spectrophotometry, is a non-exclusive method and is ideal for the detection of all carbon-containing compounds, including active ingredients, excipients and detergents.
➤ The sensitivity of the TOC method can be as high as one part per million, and compared with HPLC and UV / Vis spectrophotometry. With no need to explore the active ingredient detection methods and consider the factors of the sample, more time-saving advantages
| method | Exclusive | Drug residue | excipient | detergent | Biological Products |
| HPLC | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| TLC | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TOC | no | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| spectrum | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| PH | no | Yes | |||
| Conductivity | no | Yes |
TOC = actives + excipients + detergents + organic matter in the water system
Chapter II Comparison of HPLC and TOC methods
Here for the HPLC and TOC to explain:
First, TOC and HPLC comparison
| HPLC method | TOC method |
| l Every organic compound has special pertinence The HPLC method requires every single experiment Sensitivity (subject to detectors and compounds) l can detect insoluble in water substances l recognized methods, widely used | Targeting is all organic matter, because all organic matter is oxidized A TOC method to deal with all the experimental process, without setting other parameters High sensitivity ( 1ppb C ) A small number of water-insoluble organic compounds can also be detected l Accepted by manufacturing verification |

Important matter
➤ Specific Compound Experiments
➤ Use organic solvents
➤ Calculate based on compound lower limit
➤ Limited compound dissolution
➤ Release useful end products
Fatal shortcomings
➤ Limitation of HPLC sensitivity
➤ Each verification must have a separate SOP
➤ Very long startup time
➤ Long sample analysis time
➤ Many functions are not needed for CVs
➤ Handle new unknown peaks
Example :

There is no peak at the standard peak position.
Pass the cleaning verification, no problem!

1, the peak position abnormalities;
2, abnormal unknown peak;
Can not pass the cleaning verification, while the FDA request to confirm the unknown peak! Confirm the tedious work.
Third, TOC instead of HPLC
➤ HPLC is more difficult to use and every organic compound must be validated
➤ There are no problems with unknown HPLC peaks
➤ TOC is easy to verify
➤ The TOC can be used after the device is scratched or used for the final rinse water
➤ TOC Based on "Lower TOC in Worst Case"
➤ Equal upper limit of carbon concentration of target compound (not equal to compound)
➤ The sum of all organic contaminants must be less than the lower limit
( Clean validation of HPLC to TOC probe conversion, very easy to do)
➤ Converts the sum of total organic carbon at the target compound concentration that has been determined in the lower limit of HPLC.
➤ If necessary, adjust the cleaning procedure to ensure that the TOC is below the TOC lower limit.
Fourth, the TOC advantage
Means using organic matter as a proprietary substance, regardless of its source (including products, detergents, chemicals, solvents, by-products and microbial contamination), to determine if any residual material is present and to do so well using TOC analysis , Any active pharmaceutical ingredient or residual substance for cleaning can be detected as long as its molecular structure contains carbon. The test results must be lower than the limit of the target compound, to improve the stringency of cleaning validation.
Fifth, TOC to detect regulatory support
➤ "However, unlike residue from the final product, after cleaning, we expect no (or very low for very sensitive analysis) detergent residues."
FDA Guide to Inspections of Validation of Cleaning Processes
➤ The FDA has accepted the TOC method in its regulatory guidelines for the detection of contaminants.
➤ Appendices to PDA Technical Reports Nos. 29 and 49 refer to the TOC method and the substitution of the exclusive method for new cleaning
The worst-case method used in this document focuses on possible residues (detergents) at the end of the cleaning process. However, it is common practice to use stains in the process, or substitutes for similar drugs or compounds of interest.
It is strongly recommended to use TOC analysis in cleaning validation:
◀ Relatively low initial investment and low operating and maintenance costs
◀ easy to use, easy to train new users
◀ Extremely high sensitivity enables the detection of low concentrations, low cost compared to other methods and the ability to detect all residual materials containing carbon
◀ Fast analysis time.
◀ interference is minimal
◀ Increase equipment turnaround time.
The third chapter TOC analysis method verification
First, the analysis method validation requirements
Analytical methodological validation includes linearity, limit of detection (MD), limit of quantitation (COG), accuracy, accuracy, and wipe recovery.
Refrence: USP <1226> and ICHQ2 (R1)
➜ Validation can only be passed if the analytical method is reliable and repeatable.
➜ USP <1226> and ICH Q2 (R1) describe the validation procedure for the analytical method.
Second, TOC analysis method to verify the premise: TOC analyzer performance confirmation
➤ Analytical instrumentation validation is a process that ensures that analytical methods are used for the specific test for the intended purpose.
➤ According to the cGMP regulation, "The accuracy, sensitivity (limits of detection), specificity and reproducibility (accuracy) of the test methods used by the establishment must be established and documented." In this case, the TOC method Prior to testing the process validation, it is important that the analytical instrument be rigorously validated. This method includes installation confirmation, run confirmation, and performance confirmation (IQ / OQ / PQ) recommended by USP <1058>.
"Chinese Pharmacopoeia" (2015 edition) four 0682 Determination of total organic carbon in pharmaceutical water
Third, the system suitability test
Requirements: Response efficiency should be 85% ~ 115%.
Reagents:
➜ Sucrose standard solution (carbon content 0.500mg / L)
➜ 1,4-p-benzoquinone standard solution (carbon content 0.500mg / L)
Fourth, analysis of the key points of verification
➤ Specificity (% carbon)
➤ Linearity: 5 points
➤ Range: The concentration range between the highest and the lowest
➤ Accuracy: (total organic carbon)
➤ Accuracy:% RSD percentile standard deviation
➤ Minimum detectable limit (LOD), lowest limit of quantitation (LOQ)
➤ Reliability: under different conditions of use
Five, TOC method to verify the specific content
➤ Specific
Specialization: Specialization is the ability to determine the exact substance under test. ICH Q2 (R1) The ability to accurately quantify a target substance, organic carbon, shows that this analytical method is specific to organic carbon. This can be done by examining some of the organic-optional organic compounds that contain elements other than carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, such as organic compounds that contain chlorine, sulfur, nitrogen, or phosphorus
Example: FDA Defect Example
"Your firm failed to establish and follow writtenprocedures to assure the cleaning and maintenance of equipment used in themanufacturing of drug products. Cleaning validation for the CIP process vessel, which is utilized inthe aseptic formulation of the CIP process vessel, which is assuming in theaseptic formulation of trivalent bulk influenza vaccine ... The study did notinclude swab sampling of the product transfer lines. "
Your company failed to establish and follow written rules and procedures to ensure the cleaning and maintenance of equipment in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. For example, the flu vaccine's CIP process tank cleaning validation did not include swab sampling on the production line.
➤ Linearity and Range
Linear: refers to the measurement results and the test sample concentration was proportional to the extent of the relationship.
Range: Refers to the interval that can reach certain precision, accuracy and linearity, the test method is suitable for the upper or lower limit concentration or quantity.
定 Quantitative tests should be performed on at least 5 concentration ranges and include the minimum and maximum levels of cleaning.
The linear correlation coefficient should not be less than 0.98%.
➜ The concentration range should reach 50% -150% of the residue limit.
➜ The rinse method and swab method do not require linear / range validation for limit testing.
Example: Correlation of TOC measurements with target concentrations
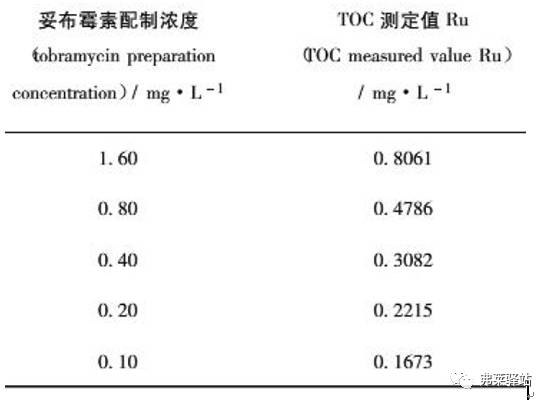
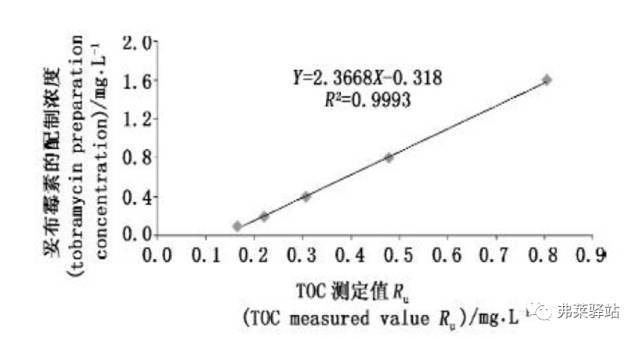
References: Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis 2013.33. (3)
➤ Precision and accuracy
To show the precision and accuracy of the TOC method, test 10 times with 10-6 carbon standard solution . The use of this carbon concentration here to assess the precision and accuracy is usually the residue of the TOC limit is generally about this level. At this TOC level, the precision is 1% and the accuracy is ± 5%.
➤ Recovery test
Determining suitable sampling methods (rinsing methods, wiping methods, sampler training and testing methods) allows for the effective recovery of contaminants / residues, ultimately providing evidence for verification.
The recovery rate and reproducibility of the sampling process were verified by the recovery test.
The sampling rate is usually combined with the recovery rate of the test method.
Ø sampling method
| method | Wipe method | Rinse method |
| definition | An inert material (usually raw cotton or similar) is attached to one end of the probe, using it to cross-rub the surface of the system. | Take the lowest drain on the rinse line. |
| advantage | Ø Areas
difficult to clean and fairly easily accessible can be evaluated so
that the level of contamination or residue for each given surface area
can be determined. Ø Insoluble residues can be sampled by physical excision. | Ø Large area sampling. Ø Systems that can not be reached or routinely uninstalled can be sampled and evaluated. |
| Disadvantages | Ø Not easy to implement on large equipment. Ø The results obtained from the small area are extrapolated to the entire product contact surface of the device. Ø It is not easy to sample hard-to-reach areas. | Ø Residues or contaminants may not dissolve or clog in the equipment. Ø Affected by the solubility of the sample taken. Ø It is unacceptable to simply test the quality of the flushing water (whether it meets the testing guidelines) without detecting potential contaminants. |
Acceptable standard recovery rate: ≥50%
Reproducibility: ≤20%
Example of steps:
1, Prepare a 500 mm × 500 mm smooth flat stainless steel plate.
2. Draw a square of 400 mm × 400 mm with a steel cone on the steel plate to form 16 blocks of 100 mm × 100 mm every 100 mm.
3, the preparation of a concentration of 160 mg / L of tobramycin aqueous solution into a quantitative spray.
4. Spray about 10 mL of solution as evenly as possible over a 400 mm × 400 mm area.
5. Calculate the amount of tobramycin per unit area based on the amount of solution actually sprayed at about 1 μg / 100 mm2.

| 1 | 2 | ||
| 3 | 4 | ||
| 5 | 6 | ||
| 7 | 8 |
7, moistened cotton swab with water for wiping Sampling procedures wipe a square each tile, 100 cm2 for a cotton swab. Take a uniform 8 squares on the steel plate.
8, the cotton swabs were placed in the test tube quantitative injection of water 10 mL, stopper and gently shaking the tube and place 10 min, the material was dissolved. The solution is then diluted 10 times.
9. Use the TOC analyzer to determine the TOC value for this cleanliness verification water sample.


10, calculate the recovery rate.
Wipe recovery rate (%) = 0.8914 / 1 × 100% = 89.1%
Take into account the actual calculation of the correction formula

CONCLUSIONS: The ideal recovery shows that the TOC analysis method is suitable for clean validation testing of target compound wipes.
Ø Wipe technology
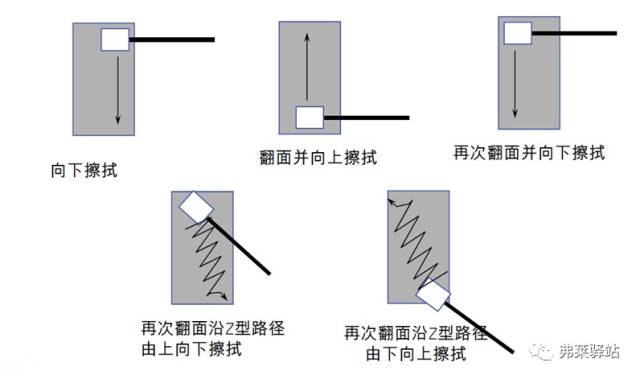
Note: Coherence, fixed force, speed and line.
Ø leaching recovery rate
Usually leaching limit inspection does not need to do the recovery rate verification, quantitative inspection should be done to verify the recovery rate. The recovery can be determined by rinsing the eluted solvent with a known amount of analyte (in the vicinity of the limit), and the recovery should generally be no less than 95%.
Rinse samples can be directly detected on the rinse solution, but also on the rinse diluted dilution test, whether direct or diluted testing should be received after the first sample with a blank solvent visual inspection to determine whether there is a color difference and foreign body Existence, if the described phenomenon occurs, you can directly determine the sample failed.
Recycling rate of acceptance
| Test Results | Evaluation |
| > 80% | 1. Acceptable 2. Good sample collection method |
| > 50% | 1. Theoretically acceptable 2. Need to evaluate whether it can be improved |
| <50 span=""> | 1. Unqualified 2. And need to investigate |
LOD / LOQ deduction method
Record the measured TOC values and standard deviations of purely standard samples at low concentrations (with 250,500, 750 ppb TOC of sucrose)
The least squares linear regression algorithm is used to determine the standard deviation of the standard versus the measured concentration equation; determine the Y-axis as the standard deviation and the X-axis as the depth.
According to regression analysis to determine the line's Y-intercept
The Y-axis intercept represents the standard hypocrisy for zero analyte concentration (Y-intercept = │S0│)
Calculate the detection limit (LOD = │Y-axis intercept │ × 3)
Calculate the detection limit (LOQ = │Y-axis intercept │ × 10)
References: Taylor, John K, Quality Assurance of Chemical Measurement Lewis Publishers imprint of CRC press (1987)
Six, TOC analysis method of attention
It is best to use a calibration curve, that is, whether the linear correlation between TOC and target concentration is good. Because each organism oxidation efficiency is different. (Unless the oxidation efficiency, can be ignored)
➜ The wipe method requires both the control solvent (eg, water for injection) and the blank swab to wipe the blank coupons for TOC analysis to determine the degree of interference.
➜ You must select the principle, TOC analyzer with the proper range. Because the water samples for cleaning validation are different from the water for injection, the cleanliness of the water sample can not be predicted.
This article Source: Fly Inn

No comments:
Post a Comment